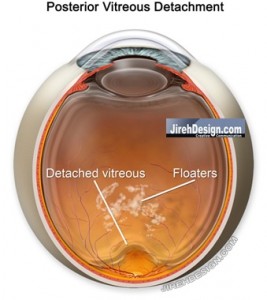
 A PVD, or Posterior Vitreous Detachment, is a naturally occurring event and will eventually happen to everyone. The vitreous, the watery gel, which fills the posterior portion of the eye, is composed of protein and mostly water. The vitreous is not regenerated and is a vestigial tissue.
A PVD, or Posterior Vitreous Detachment, is a naturally occurring event and will eventually happen to everyone. The vitreous, the watery gel, which fills the posterior portion of the eye, is composed of protein and mostly water. The vitreous is not regenerated and is a vestigial tissue.
With time, the vitreous proteins degenerate, hydrolyze or liquify. The posterior portion of the vitreous separates, or detaches, from the surface of the retina. Symptoms of a PVD usually include flashes…and floaters.